durty shows you the future of Whiteout…
Tag Archives: Video game
Editors Note: Another Historical Moment for the BOOM!
Editor’s Note: The article below represents another historical milestone for the BOOM for numerous reasons. Over the past few months, we have noticed, in our traffic results, a sharp increase in visitors from China, and the Orient in general. While we anticipated a Japanese appreciation for our work, and have translated articles into their language, we did not expect the remarkable response from our video gaming sisters and brothers from the motherlands of China and Vietnam. You are, both, most welcome to the BOOM.
In honor of their extraordinary participation, we have decided to translate some of our future articles into other languages of the East. Our first, is a translation, into Mandarin Chinese, of our most popular series to-date: “The Panopticon in My Bedroom: Parts I & 2.” It is our way of saying “Thank You” for coming to the BOOM, and allowing us to inform and entertain you.
-BOOM
Mandarin Translation of the above:
THE ROOM: An Architectural Theory of the Future Technological Foundations of a VR Universe.
In a recent GAMESPOT article, Strauss Zelnick, the CEO of Take-Two Interactive, encapsulated in a single sentence, the greatest challenge ahead for Virtual Reality. He said, “…there is no market for [an] … entertainment device that requires you to dedicate a room to the activity.” He, then, went on to identify the second major issue, when he jokingly said, “We don’t have a [room] where you stand in a big open space and hold two controllers with something on your head—and not crash into the coffee table. We don’t have that.”
And that my friends, is why Mr. Zelnick, though admittedly not a “gamer,” makes the big bucks.

As progeny of the television-centric home entertainment ecosystem (HEe)[1] we have grown accustomed to staring at moving pictures on walls (see Figure 1), and not moving while we do so. Certainly there are times when movement is appropriate and expected, but in order to fit within the HEe it must be anticipated, and changes made to accommodate the increased need for space and separation. In other words, you need to move “the coffee table” so no one gets injured.
But in most cases, we watch TV, not moving, and, often, reclining. In fact, there have been numerous studies conducted by the manufacturers of video and audio equipment that indicate the best viewing angle, and thus seating position, for the consumer to fully enjoy a, so-called, “immersive,” entertainment experience. VR will eventually demand more.
In this, the first of a two-part series of the BOOM, I examine the problems inherent in the VR experience, as a duplication and augmentation of reality, in the context of spatial dynamics (the ROOM), room orientation, stabilization, and finally, sound presentation. It is around these fundamentals, along with several others, that the foundations of true, cognitive envelopment, necessary to convince our minds we are really somewhere else, may be established.
BOOM Salad 出品:durtyrezkidz, 也称为”TURBO AJ LITTLE BIRD.” 枪林弹雨!
BOOM Salad Presents: BOT RAGE!!!!!
From Peripheral to Preeminence: The Rise of the Video Media Console, Part III, “From arcade to VR ecosystem.”
Those that grew up during what I have often referred to as the “Golden Age” of video gaming,[1] remember a time when there was no preference between PC and console. There was just gaming. In fact, there are some games that we loved every bit as much as our favorite PC, console, and arcade games, which are now, all but forgotten.[2] Still, as for where most gamers of the period, young and old, preferred to play their favorite games, the arcade was king (see Figure 1).

Though the graphics and gameplay of the standalone machines were often identical to their console/PC versions, there were a lot more games to play at the arcade then at home or school. Also, there was an energy in the place that was palpable and electrifying.[3] Playing in the arcade during the decade of the 1980’s could be viewed as a prototype of the multiplayer experience that we now enjoy online, with one big difference: back then we played, physically, side-by-side, every time.
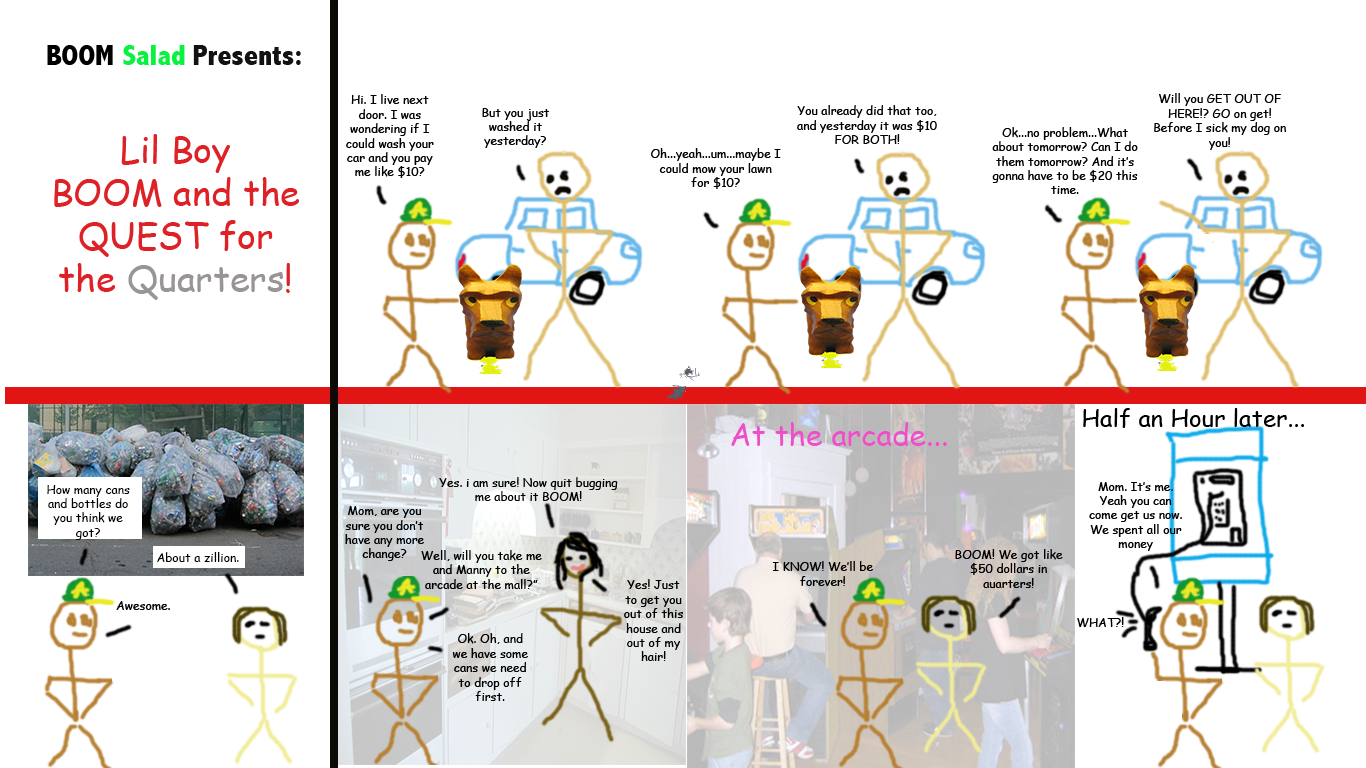
While the arcade may have been our preference, there were two, significant, disadvantages: cost, and the fact that you needed transportation to get to one. Both reasons made it an impractical, though highly desired, option for me and my eight and nine-year-old, school friends. Even after washing everyone’s car on the block, mowing their lawns, scavenging for and returning bottles and cans for the deposit, and, finally, squeezing your parents for every last quarter they had, it didn’t take long to burn through your hard earned change once you walked into that neon-lit, multisensory extravaganza of light, sound, and movement (see Figure 2). It is largely for these reasons that the console became our video gaming method of choice.
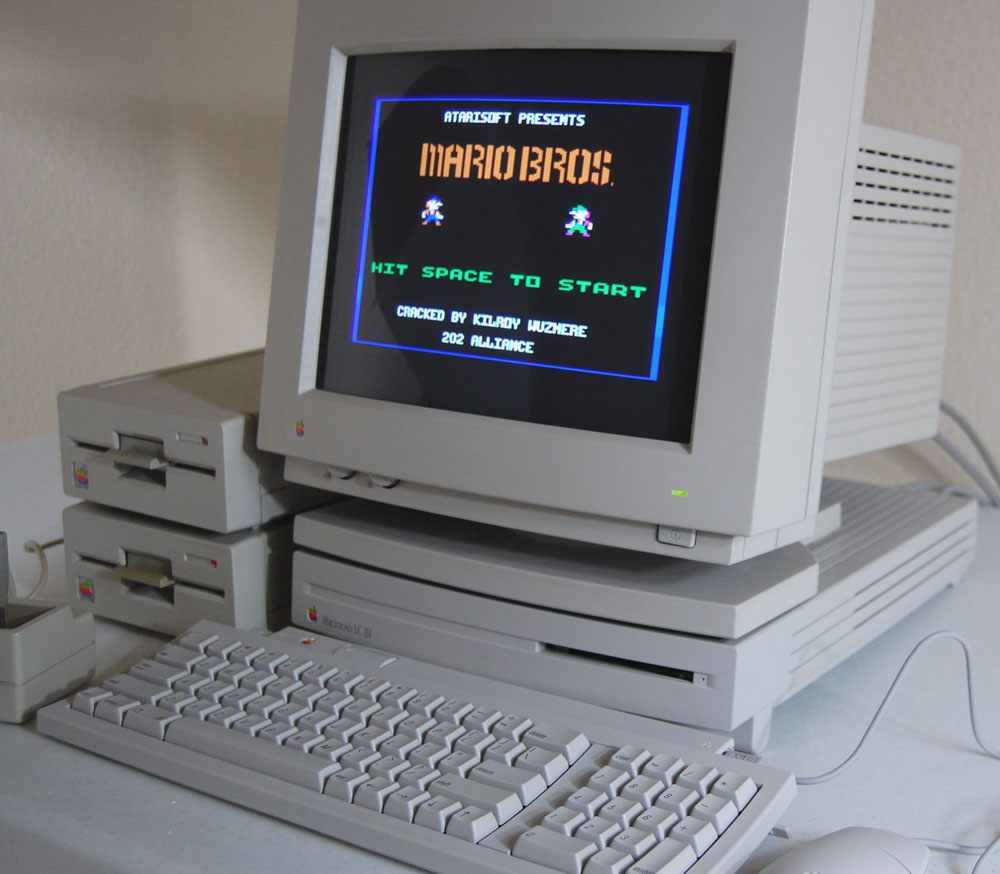
Thus, it was during the decade of the eighties that video gaming as a practice and event shifted from the surrealistic environment of the arcade to become a more home-based activity in which the console played a dominant role. At the time, PC’s were also in their infancy. Companies like Apple, and even HP, had demonstrated an early interest in video gaming software development, but purchasing their hardware was expensive, often more expensive than a console (see Figure 3). Moreover, PC’s were still, for the most part, considered business machines and not video gaming platforms. For many gamers, therefore, the console was the only realistic option.

This economic ‘reality,’ in many ways, created a division between the gamers that had access to a PC, and those that could only get their hands on a console. From this point forward, the question of which platform, PC or console, was technologically superior, became the subject of a debate that continues, thirty years later, into our current day.
Of course, the rift between PC and console gaming is more complicated than the “debate” over which is a, “superior,” platform. However, no one would dispute that this is the primary issue that continues to surface and resurface whenever gamers argue over which is best for gaming. Now, it seems, this age old argument has been given new life in the discussion over which is a better platform for delivering Virtual Reality (VR).
As recent as this past February, Tim Bajarin, a well-known, well-respected technologist, “futurist,” and contributor for PCMag, revealed how this divisive issue is being used to influence the direction of VR software development. In his post, “Why Sony Has a Big Lead in VR,” he offers reasons why the PC is a more preferable VR appliance than the Playstation, or any other console. The primary concern, as he sees it, is the console’s seeming, one purpose functionality as a gaming device. According to Mr. Bajarin, consoles like the Playstation 4, “[are] largely gaming platforms.”
BOOM Salad Proudly Presents: durtyrezkidz, a.k.a “Turbo Aj Little Bird.” The Sky is Falling!
 Rarely does one get an opportunity to witness what happens when total mastery over fundamentals intersects with raw talent. And yet, that is exactly what has happened: lightning has struck the BOOM twice!
Rarely does one get an opportunity to witness what happens when total mastery over fundamentals intersects with raw talent. And yet, that is exactly what has happened: lightning has struck the BOOM twice!
It is with great pride that I announce to our readers, the BOOM’s latest sponsee: durtyrezkidz, a.k.a. “Turbo AJ Little Bird.”
He is simply the BEST Little Bird pilot we have ever seen, a remarkable statement considering our past experience. Come watch and be amazed…the sky is falling.
From Peripheral to Preeminence: The Rise of the Video Media Console, Part II, “And the Winner IS…”

Since the release of FB-Oculus‘[1] first of, what I expect will be, numerous iterations, of its mind-bending, reality-shifting, VR apparatus, much has been said by the mainstream media (Vox, Wired, New York Times, etc.) about the future of VR, and its immediate and long-term impact on the way in which we consume media. And while we at BOOM Salad are gratified to see these touchtones of 21st century, online journalism finally affirm something that we stated conclusively more than a month ago, it is clear that they are still struggling to understand the far-reaching implications of a world permeated by VR technology. By that I mean, VR is not 3-D Television. VR is legit, it’s coming, in fact, it’s here, and Oculus is just the beginning.
Unlike other entertainment devices, the uses of VR will not be confined to the realm of video-related entertainment. It will continue to evolve beyond its original focus to include whatever need or desire we have for a virtualized universe. In other words, there is no aspect of society that does stand to be affected in a significant way: education, politics, commerce, medicine, and of course, ART. VR has the potential to redefine the way in which humanity consumes reality.
A simple illustration: for the past two decades, most of the world’s greatest cultural centers have labored, with the best of intentions, to provide an immersive online environment via the web (see Figure 2). They have all failed for the same 2D reasons. With VR, their dream: to deliver an immersive, first-person-experience to anyone, anywhere in the world, just took its first big step forward to becoming a reality. Well, a virtual reality at least.
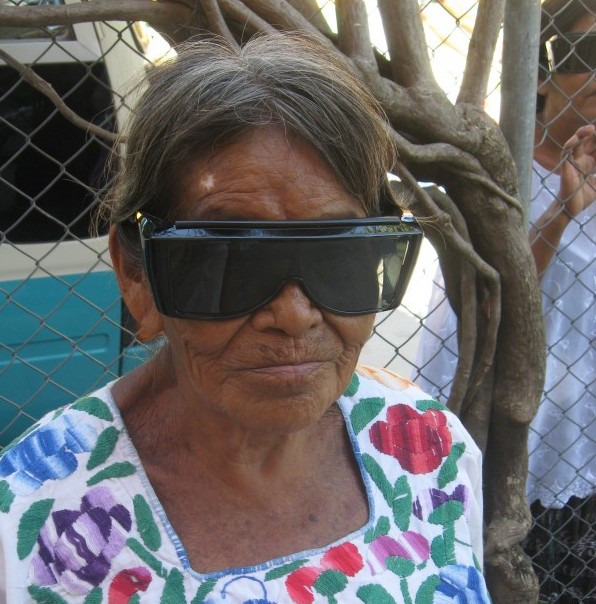
Still, it will take more than a fancy headset that looks like your grandmother’s UV shields (see Figure 3) for the promise of a VR universe to be realized, and this is where other media sources seem hopelessly unaware. The most important component of the VR paradigm is not the magic goggles. Nope. An Oculus would be nothing without a delivery device to feed it content (see Figure 4).

BOOM Salad Thanks King-Dylan666: The Paganini of the First-Person-Shooter.

At the end of last fall, BOOM Salad entered into an historic agreement to become the first to sponsor the Battlefield 4 player known as KING-DYLAN666.[1] Since that time, we have been honored to reveal to the world, via this website, his near inhuman playing skills on the battlefield. Time and again, in video after video (see below), the KING has demonstrated conclusively that he is one of the best in the business. He is a machine, a true 21st century gaming freak of nature, and yet, some in the online gaming world have sought to undermine his place amongst the elite, by criticizing the amount of time the KING has played the game for which he has become well-known.

According to his Battlelog profile, KING-DYLAN666 has spent a total of 9,320 hours playing Battlefield 4 (PS3 and PS4 combined). If one assumes he began playing on the date of the game’s release in 2013, that would mean he has played, on average, more than 10 hours a day, for nearly two and a half years!
But I know what some of you are thinking, because, for the past six months, we’ve heard it all:
“What a loser!”
“Damn Daniel! That man needs to get a life!”
“I bet he’s a virgin.”
Naturally it is hard for some to fathom the kind of dedication that the KING has put into an activity that continues to be miscategorized by society as a form of casual entertainment. By this I mean that the criticisms leveled at KING-DYLAN for the amount of time he has spent perfecting his skill, reveal an outdated view of video gaming that fails to recognize its increasing complexity as a practice. Moreover, such statements also demonstrate a disappreciation of the physical ability required to achieve the level of dominance exhibited by the KING.
The Uncanny Violence of Video Games, PART IIa: “The Thin Red Line Between Violent- and Competitive-Aggression.”
Editor’s Note.
Towards the end of the twentieth century, medical researchers and behaviorists all over the world were looking at the similarities between so-called, “violent media,” such as film and TV, and video games that depicted violence in their gameplay. For many, and certainly all of those who generously gave their time to BOOM Salad in interviews, and other assistance, their motives were simple, protect those who are amongst the most vulnerable in society: children and young people. For this reason, BOOM Salad acknowledges and honors the efforts of these women and men of science, and others who have sought to shine a light on why and how video games affect those that play them, why they make us go “BOOM!” as it were, and the corollary effect of video gaming on society in general.
Over the past few months, BOOM Salad has interviewed several researchers considered to be amongst the first to study the relationship between behavior and video games, including Dr. Vincent P. Matthews, Chair of Radiology, Medical College of Wisconsin; Dr. Yang Wang, Associate Professor, Medical College of Wisconsin, Division of Imaging Sciences; and Dr. Brad Bushman, Professor of Communication and Psychology, Ohio State University. The premise of their investigations was based on the assumption that violent-video games are a genre of violent media (see the clinical definition of “violent media” below). As such, previous research suggested that high exposure to violent-video games would likely cause increased aggression in cognition, affect, and arousal. From this starting point, researchers were able to rely on the confidence of medical studies conducted over the past 60 years that have consistently demonstrated the causal relationship between high Violent Media Exposure (VME) and aggressive bias and behavior.
Like their predecessors and contemporaries, the individuals we spoke with were world-class researchers with sufficient funding to establish the credibility of their results. Thus, to challenge the veracity of their findings would be misguided and unfruitful. That is not to say that we agree with their conclusions, quite the contrary, we do not, and for what we believe to be good reasons.
In the following, Part IIa and IIb of the Uncanny Violence of Video Games, BOOM Salad will demonstrate a fundamental error in the theory at the heart of the anti-violent video game argument, while at the same time offering an alternative hypothesis as to how and why these games affect our behavior. Our goal, much like that of the doctors we interviewed, is to root out the cognitive and behavioral context that underlies the ever-increasing fascination with video games in global society. Only by understanding what compels individuals to play the games, can we better determine how it is affecting them and their behavior.
As always, it is our Primary Objective that you will enjoy and be challenged by our efforts. – BOOM.

How do we determine how someone is feeling? One way, is by examining his or her expression (see Figure 1). Do they look happy, or sad? Are they smiling, or are they frowning?
Another way is through listening to their voice and analyzing their vocal expressions. Do they sound happy or angry? Are they saying words that would indicate happiness or aggression? Through these and other clues, humans “predict” the feelings and actions of those around them.
But even with the availability of all this visual and auditory data, we can never be 100% sure how someone is feeling. Why? Because emotions are “unobservable states” that “dynamically change”[1]. In other words, emotions cannot be viewed directly, we cannot see into a person’s psychology and understand, as they do, how they are feeling. Moreover, emotions can change in an instant.
For example, when we consume visual media, like film and TV, it is not unusual to feel different emotions as the program progresses. At one moment we are fearful, and then another, hopeful or relieved, and perhaps even at the end, we might feel happy or euphoric, all within the span of two hours. The Entertainment industry relies on this powerful ability to visually and emotionally engage its viewers, as a form of incentive to pay for its products.
Given this, the best we can do in assessing how one is feeling at a particular moment in time, is in observing and interpreting her or his behavior and mannerisms. Most of the time, this is sufficient to accurately assess someone’s current emotional state, but because of our own limitations to perceive the “unobservable,” we make mistakes resulting in a misinterpretation of a person’s actual feelings.
To increase the reliability of these observations, medical researchers and behaviorists have developed a number of theoretical models. One of the most important of these is known as the “reinforcement learning model (RL)”[2]. The RL provides a useful methodology to understanding so-called, “rewards-based behaviors.”
According to the RL, rewards provide an incentive that leads to what is known as, “operant conditioning,” in which a person will voluntarily change her or his behavior and behavior paradigm to receive a reward . For example, a child is promised a reward if she or he does well on a math test (see Figure 2). To attain this reward, the child voluntarily changes her or his behavior by studying more or paying more attention to homework assignments. When the reward is received, these changes in behavior become part of the behavioral algorithm used by the child to determine her or his actions in a given environment.